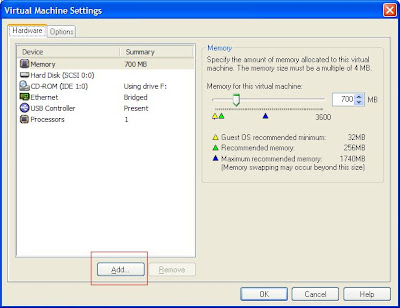
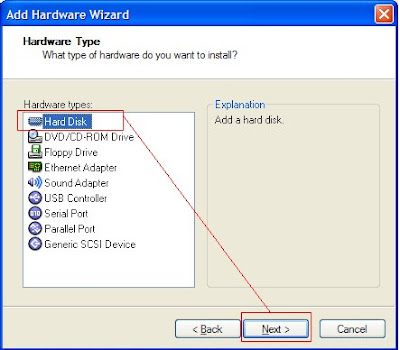
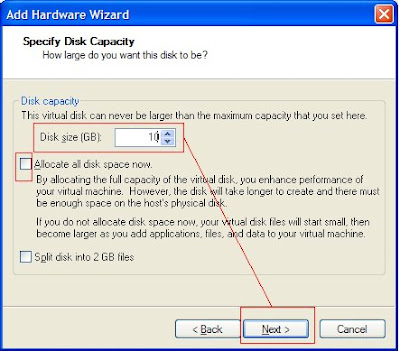
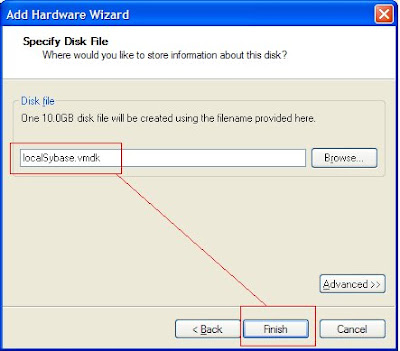
Operating System: Virtual Machine: Oracle Enterprise Linux 5.2 (32-bit)
Oracle RDBMS Version: Oracle 11g - 32 bit for Linux
This is the error due to SE Linux running in Enforce mode. The best way to avoid this is – make the SE Linux in Permissive mode. This can be done at the time of Setting up your server (by not selecting the security feature) (or) once the server setup completes you can set the value to 0.
Refer Metalink Doc Note:454196.1
 **********************************************************************************
**********************************************************************************
sqlplus: error while loading shared libraries: /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1/lib/libnnz11.so: cannot restore segment prot after reloc: Permission denied
[oracle@oracle11g ~]$
I could able to solve this, by following the above Metalink Document. Hope this helps you.
[oracle@oracle11g ~]$ sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on Fri Aug 22 15:30:06 2008
Copyright (c) 1982, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to an idle instance.